
How to Disable IPv6 on your TPLink Router (v1,v2,v3)
This tutorial provides the steps required in order to disable IPv6 on your TPLink Router, Interface version 1, 2 and 3 being the latest software release.
Before you start: It is always recommended to backup your router configuration prior to making any changes that may impact the operational components of your system.
TPLink Version 3
Connect to your Routers UI via a Web Browser
Open up your favorite web browser and navigate to the default gateway of your TPLink router. This address is typically http://192.168.1.1.
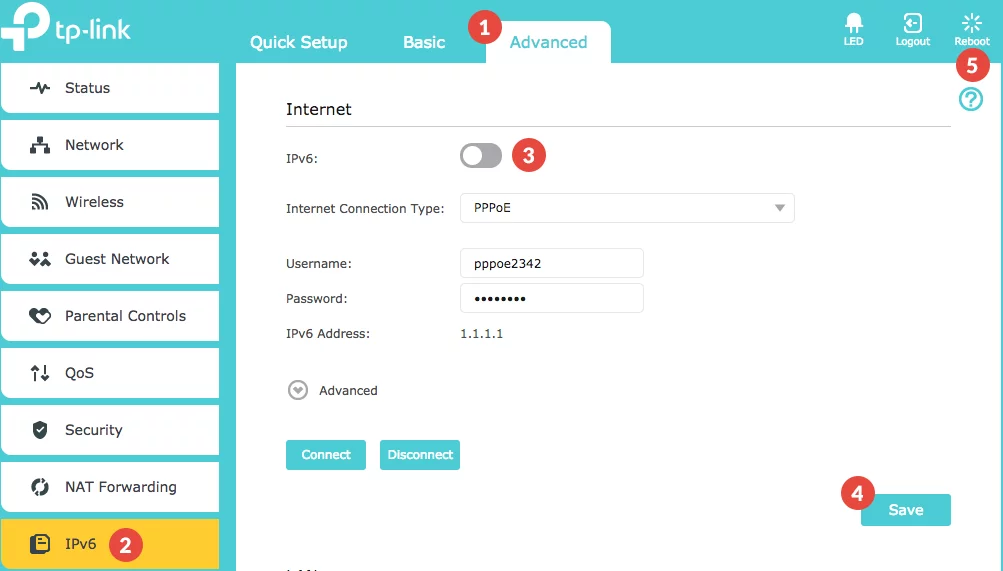
Step 1 – Click on the Advanced tab
Step 2 – Navigate to the IPv6 option in the left navigation menu
Step 3 – Press the IPv6 switch to the off position
Step 4 – Select “Save”
Step 5 – Reboot your device
TPLink Version 2
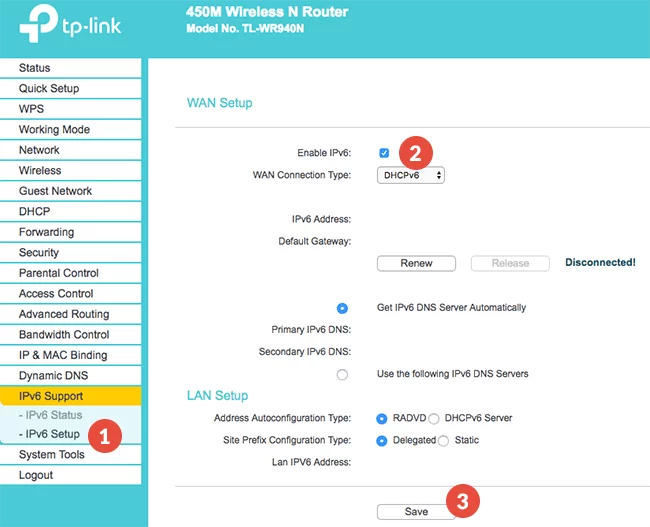
Step 1 – Navigate to the IPv6 Support tab menu -> IPv6 Setup
Step 2 – De-Select the Enable IPv6 checkbox
Step 3 – Save Settings
Step 4 – Reboot Router
TPLink Version 1
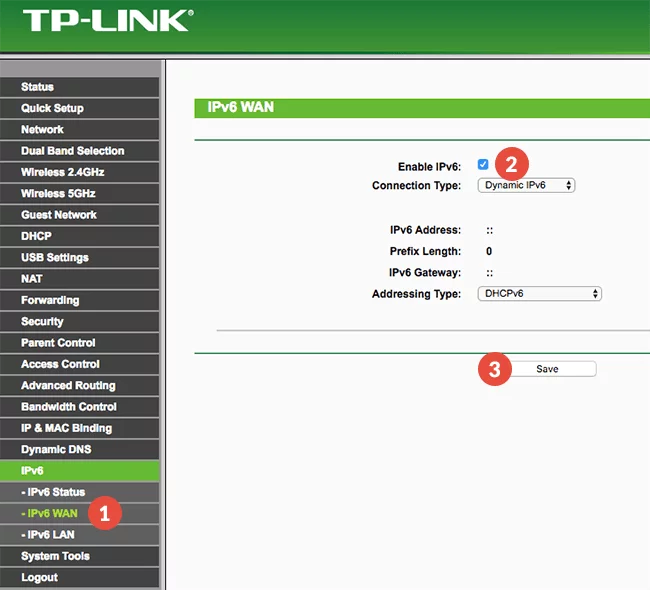
Step 1 – From the Navigate menu, select IPv6 -> IPv6 WAN
Step 2 – De-select the “Enable IPv6” checkbox
Step 3 – Save settings
Step 4 – Reboot Router
Q: What is IPv6
A: IPv6 is the next generation Internet Protocol (IP) address standard intended to supplement and eventually replace IPv4, the protocol many Internet services still use today. Every computer, mobile phone, home automation component, IoT sensor and any other device connected to the Internet needs a numerical IP address to communicate between other devices
Q: What are the benefits of IPv6
A: IPv6 is the sixth revision of the IP protocol and is the successor of IPv4. If functions similar to IPv4 in a sense it provides a unique IP address to a device in order to access the internet. However, it does have one significant difference: it utilizes a 128-bit IP address.
IPv4 uses a 32-bit address for its Internet addresses. That means it can provide support for 2^32 IP addresses in total â around 4.29 billion. That may seem like a lot, but all 4.29 billion IP addresses have now been assigned, leading to the address shortage issues we face today.
IPv6 utilizes 128-bit Internet addresses. Therefore, it can support 2^128 Internet addresses—340,282,366,920,938,463,463,374,607,431,768,211,456 of them to be exact. The number of IPv6 addresses is 1028 times larger than the number of IPv4 addresses. So there are more than enough IPv6 addresses to allow for Internet devices to expand for a very long time.
Q: Why am I being force to use IPv6 over IPv4
A: As stated in the previous response, IP availability. IPv4 addresses are being utilized more than ever with the number of connected devices in the home increasing, eventually this will lead to global IPv4 exhaustion. Governments and ISP are working collectively to try implement IPv6 support by transitioning your home internet connection to dual stack (both IPv4 and IPv6).
Q: Why are you asking me to disable IPv6 for Smart DNS
A: When your Internet provider assigns your device a dual stack IPv4/IPv6 IP, more often the device will prefer IPv6 and as a result will query using the IPv6 ISP provided DNS servers, not DNSFlex IPv4 DNS. This leads to service interruptions and frustration. We always recommend disabling IPv6 to ensure the highest level of reliability and performance when using Smart DNS services.


